At Home physiotherapy After Paralysis (Stroke)
Call Us: +91-9421750231, +91-7875411115.

what is Paralysis (Stroke)?
physiotherapy of paralysis, the patient is Loss of motion is the deficiency of muscle work in a piece of your body. It happens when something turns out badly with the route messages to pass between your mind and muscles. Loss of motion can be finished or incomplete. It can happen on one of the two sides of your body. There can be numerous foundations for loss of motion however are frequently brought about by strokes, ordinarily from an impeded corridor in your neck or mind. Some other basic causes are nerve injury, poliomyelitis, numerous sclerosis, cerebral paralysis, Parkinson’s infection, spina bifida, fringe neuropathy, ALS, botulism, and Guillain–Barré disorder.
Since the loss of motion can influence various rates of the body and various territories, specialists order the condition into four fundamental sorts: monoplegia, paraplegia, hemiplegia, and quadriplegia. a clinical term for the complete absence of deliberate development regularly sets in during Stage 1. This loss of motion is brought about by nerve harm that keeps the muscles from accepting fitting signs from the mind, regardless of whether the cerebrum is as yet equipped for moving those muscles. physiotherapy of paralysis patient.
risk factors for Paralysis (stroke)
non-modifiable risk factors
physiotherapy of paralysis patient
- Aging & gender
- Positive family history
- Circadian and seasonal factors (peaks between 10 am till noon)
- Heart disease
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hypertension
- Peripheral arterial disease
- Blood pathology (increased hematocrit, clotting abnormalities, sickle cell anemia, etc.)
- Hyperlipidemia
Modifiable risk factors
physiotherapy of paralysis patient
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Lack of physical exercise or sedentary lifestyle
- Diet & excess alcohol consumption
- Oral contraceptives
- Infection (meningeal infection)
- Psychological factors
- Vasectomy
Stages of recovery from stroke (Paralysis)
paralysis physiotherapy Stage 1:
recovery occurs in a stereotyped sequence of events that begins with a period of flaccidity immediately following acute episode.No movement of limbs can be elicited
Paralysis Physiotherapy Stage 2:
basic limb synergies or some of their components may appear as associated reactions. Minimal voluntary movement may be present. Spasticity begins to develop
Paralysis Physiotherapy Stage 3:
Gains voluntary control of movement synergy although the full range is not developed.Spasticity has further increased
Paralysis Physiotherapy Stage 4:
some movement combinations that do not follow the synergy are mastered the first with difficulty & later with more ease. Spasticitybegins to decline
Paralysis Physiotherapy Stage 5:
more difficult movement is learnt as the basic limb synergy lose their dominance over motor roots. Spasticity further declines
Paralysis Physiotherapy Stage 6:
the disappearance of spasticity, individual joint movement becomes possible & coordination approaches normal. Normal motor function is restored.
Can A Customized physiotherapy of paralysis patient Program Help?
Positioning strategies in physiotherapy of paralysis patient
- In supine
- In side-lying on the normal side
- In side-lying on the affected side
Improve respiratory & Circulatory function in physiotherapy of paralysis patient
- Breathing exercise
- Chest expansion exercise
- Postural drainage
- Huffing & Coughing techniques
- Passive & active ankle & toe exercise
- (after careful & thorough examination of the cardiopulmonary system)
Prevent pressure sores in physiotherapy of paralysis patient
- Proper positioning
- Relieve pressure points by padding & cushion
- Frequent turning & changing position
- Prevent from moisture
- Use cotton clothing
- Tight-fitting cloth is prevented
- Use of water bed, air bed & foam mattress
Prevent from deconditioning
- Early mobilization in the bed (active turning, supine to sit, sit to supine, sitting, sit to stand)
- Pelvic bridging exercise
- Early propped up positioning, sitting & then later to a standing
- Moving around the bed
- Facilitate movement of functioning limbs

COMMON Neurological TECHNIQUES INCLUDE
physiotherapy of paralysis patients, Manual therapy effectively addresses the mechanical, biochemical, and psychological qualities of the treatment process. You’re expected to visualize a far better range of motion in stiffer joints and pain relief by improving how your brain processes pain signals. one among your body’s main systems that control pain is activated by specific muscle movements, which suggests that manual therapy can help ease in what proportion difficulty you experience.
SOME TECHNIQUES ARE:
- ICING
- Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation
- Neurodevelopmental treatment(NDT)
- Muscle Energy Technique (MET
- STRETCHES (MUSCLE, NEURAL TISSUE, JOINTS, FASCIA)
physiotherapy of paralysis patient

ICING
Ice can be used to facilitate a response from muscle. Ice uses a combination of coolness and pain sensations to produce the desired response.
In order to facilitate a motor response, an ice cube is quickly swept over the chosen muscle belly
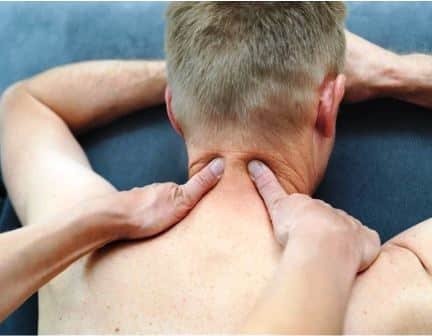
Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation
Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) is a stretching technique utilized to improve muscle elasticity and has been shown to have a positive effect on active and passive range of motions.
What does a PNF stretch consist of? There are three PNF methods: the contract-relax method (CR), the antagonist-contract method (AC), and a combination of the two – contract-relax-antagonist-contract (CRAC). CR involves contracting, holding, releasing and stretching the target muscle.
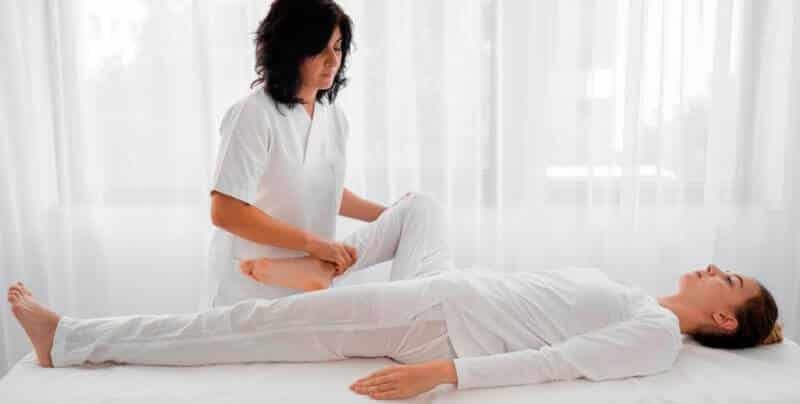

Neurodevelopmental treatment
Neurodevelopmental treatment is based on the premise that the presence of normal postural reflex mechanisms is fundamental to a motor skill’s performance. The normal postural reflex mechanisms consist of righting and equilibrium reactions, reciprocal innervation, and coordination patterns.
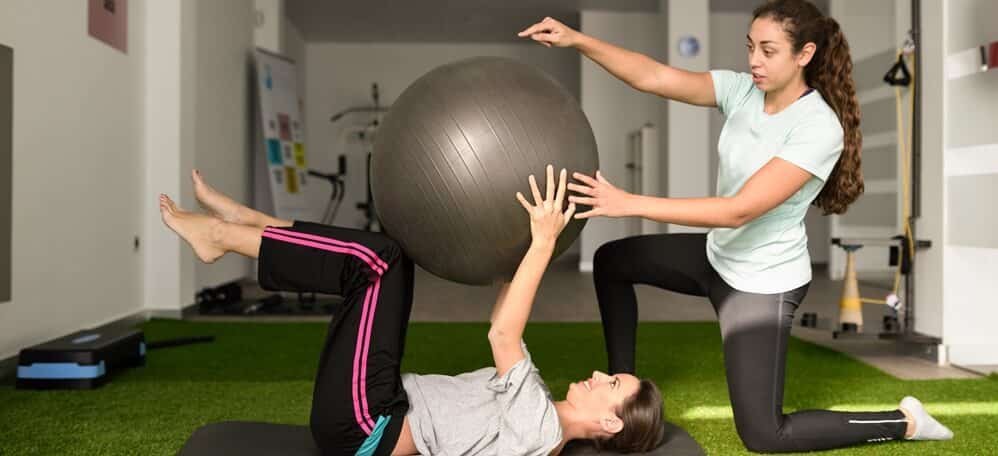

Muscle Energy Technique (MET)
Muscle Energy Technique (MET) is a technique that was developed in 1948 by Fred Mitchell, Sr, D.O. It is a form of manual therapy, widely used in Osteopathy, that uses a muscle’s own energy in the form of gentle isometric contractions to relax the muscles via autogenic or reciprocal inhibition and lengthen the muscle.
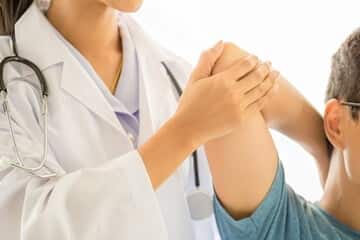
STRETCHES (MUSCLE, NEURAL TISSUE)
A physiotherapeutic passive activity in which a specific nerve, muscle, or group of muscle is deliberately stretched in the opposite direction of its activities(both directions in neural tissue) to improve the muscle’s flexibility( in neural tissue a compression) and achieve comfortable muscle tone or in nerve better conduction. The result can show an increase in muscle control, flexibility, decrease in neurological pain, and relative joint range of motion.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Can physiotherapy cure paralysis?
Although there is no cure for paralysis at the moment, daily physiotherapy of paralysis patients can help restore movement and sensation in that limb to a great extent in cases where the paralysis is caused due to factors like stroke or a transient ischemic attack.
How long does it take to recover from paralysis?
By the end of your first three months, you will have made most of the recovery that you can expect to make. Again, this is a significant divergence from SCI rehabilitation, where complete recovery can take a year or longer. The exception for stroke patients would be those who experienced damage to the brainstem.
What is the fastest way to cure paralysis?
- Clean and grind asparagus (genus) leaves and apply them to the area of pain caused by paralysis.
- For relief from Inflammation and pain due to it, Saute a few drumstick leaves in castor oil and apply to the pain area.
- Radish oil 20-40 ml twice a day daily can help in curing the condition.
Can a paralyzed person ever walk again?
People whose spinal cord injuries did cause complete paralysis may still have a good chance of muscle recovery if they have sensation in the lower part of their body just after the injury.
WHAT MAKES YOU BETTER THAN OTHER PHYSIOTHERAPISTS?
you’ll benefit from a prompt flexible service. That includes a professional assessment and diagnosis followed by a tailor-made rehabilitation program suited to your individual needs. They have extensive experience, working both in clinics and Physiotherapists’ home visits.
What are the four types of paralysis?
Because paralysis can affect different percentages of the body and different areas, experts classify the condition into four main types: monoplegia, paraplegia, hemiplegia, and quadriplegia.
How much does a session of Manual therapy cost?
The average cost of a physiotherapy session is 600 – 700 Rs. This is the average across Pune. The cost of a physiotherapy session can be as low as 500 Rs. as manual therapy is also included in the session you don’t need to pay any extra cost for manual therapy.
How do you know if you need physiotherapy?
If you had a particularly hard day at the gym, you would feel sore afterward. But if your pain is persistent and not getting any better, that is a sure sign that you need to see a physiotherapist. Likewise, mobility and movement are reasonably constant for a person. Sure, with age they change, but not overnight.
WHAT SHOULD I EXPECT ON FIRST VISIT ?
Our Physiotherapists will try to understand what your goals are, they will explain how they will assess you and ask for your consent before they start. After the assessment, the physiotherapist will explain what physiotherapy can help you with, how long it might take, and the expected outcome from the treatment.

vardenafil 40 mg https://vegavardenafil.com/ vardenafil cheap
caverject suppository https://alprostadildrugs.com/ how to adminiter transurethral alprostadil